
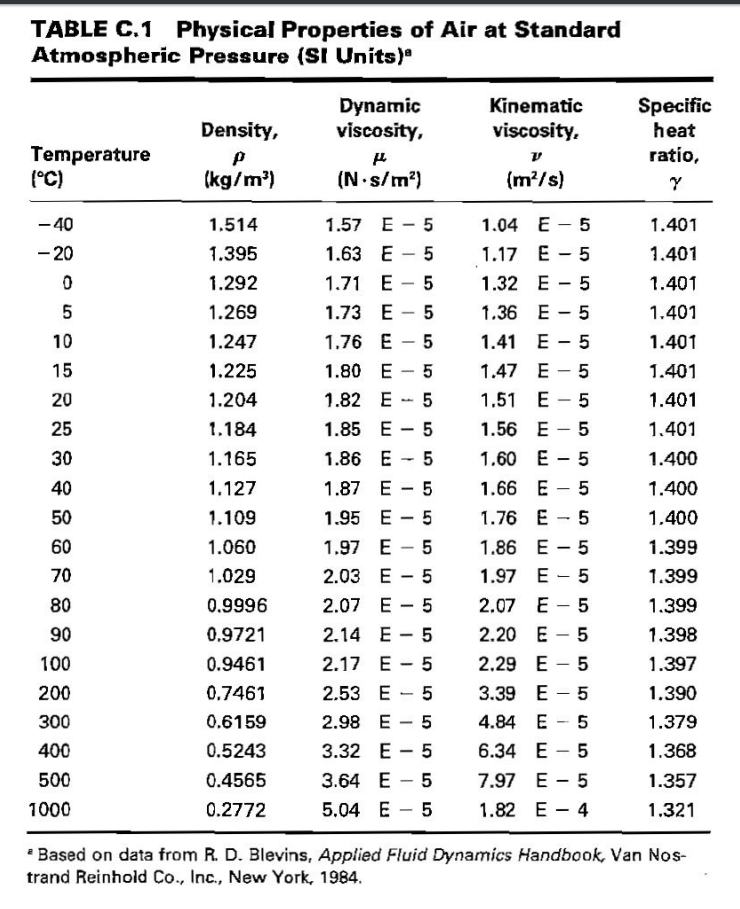
These all help to ensure more accurate results.Īfter equilibrating to the test temperature, the liquid is flowed through a capillary viscometer and the time is recorded. Some also have features to automatically calculate the viscosity, or even detect the results by optical sensors. Viscosity Baths are available in a range of specifications – models that heat, high temperature models for extended heating, or refrigerated models to run tests below room temperature. A viscosity bath is used to immerse capillary viscometers in liquid and hold them at a steady temperature – removing temperature as a variable in the test This means that accurately controlling the temperature of the liquid during testing is vital to ensure consistent results which can be compared across different batches or products.Ī viscosity bath is used to maintain samples at a steady and accurate temperature for Kinematic Viscosity testing to ensure that temperature is constant, and not a variable. You can see this effect in action by warming honey – at room temperature this is thick and slow to pour (high viscosity) but if you heat it in a pan you can see it becomes thin and fast to pour (low viscosity). The impact of temperature on viscosity is huge – for every ☌ change, the viscosity can change by 2 to 10% (depending on the liquid). very thick liquid, slow to move when it is poured) very thin liquid, flows and pours fast) to high viscosity (i.e. The most commonly used unit is centiStokes (cSt) but some methods may report in mm 2/sīelow you can see the viscosity of some common liquids – ranging from low viscosities (i.e. What units is Kinematic Viscosity reported in?

The time taken for the liquid to flow is measured – this could be the time it takes to travel through a capillary, or through a cup with a hole in the base. This is different to Dynamic viscosity, which measures the resistance of another object moving through the liquid. Kinematic Viscosity specifically is a measure of resistance to the liquid moving. Put simply, this means how thick or thin the liquid is – how easily it flows. The definition of viscosity is a measure of a liquid’s resistance to movement. We’ve explored some of the most commonly asked questions about viscosity testing what is kinematic viscosity? How is it measured? How does temperature affect viscosity? And how can you make sure your viscosity measurements are accurate? A glass capillary viscometer, used in Kinematic Viscosity measurements It is more commonly measured in centistokes (cSt).Kinematic Viscosity measurements are used in quality control and characterization tests in a wide range of fields. Kinematic viscosity has SI units of m 2 s -1. It is more commonly measured in centipose (cP). Units of Measurementĭynamic viscosity has SI units of Pa s. Kinematic viscosity measures this in terms of density, whereas dynamic viscosity does not. Difference Between Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity Involvement of Densityīoth dynamic and kinematic viscosities measure how difficult it is for a fluid to flow. When the viscosity of a substance is quoted, the temperature should be specified. Note that since viscosity depends on temperature (the viscosity decreases as temperature increases in liquids, while the viscosity decreases when the temperature of a gas increases). However, the more commonly-used unit for measuring kinematic viscosity is the centistoke (cSt). The SI unit of kinematic viscosity is m 2 s -1. Kinematic viscosity ( ) of a fluid is the ratio of the fluid’s dynamic viscosity to its density : Non-Newtonian fluids cannot be described with one value for viscosity. Note that the above equation is only valid for so-called Newtonian fluids. In this sense viscosity is a measurement of how difficult it is to make a fluid flow. is a constant of proportionality, and it is known as the dynamic viscosity of the fluid. Where is the area of the layer and is the distance between the layers. The force required to move a layer of fluid in this way is related to the velocity at which the fluid layer will move by the equation: A force needs to be applied to a layer of fluid in order to make it flow at a constant speed relative to any other layer. Whenever a fluid flows against a surface, the different layers of fluid exert frictional forces between each other, causing them to flow at different speeds. The main difference between dynamic and kinematic viscosity is that dynamic viscosity is a measurement of how difficult it is for a fluid to flow whereas kinematic viscosity is the dynamic viscosity of a fluid divided by its density. Usually, two types of viscosity are quoted: dynamic and kinematic viscosity. Viscosity is very important to any process that depends on a flow of fluid. Main Difference – Dynamic vs. Kinematic Viscosity


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
